Docker is a tool designed to make it easier to create, deploy, and run applications by using containers. Containers allow a developer to package up an application with all of the parts it needs, such as libraries and other dependencies, and deploy it as one package.
Now we might think why we need Docker concept. Lets take simple example. We have a shooing web application which has the aspect such as login/security, product catalog, Account Service, Cart Server and order Server. In best practice we prefer to have micro service either build on Spring BOOT or other frame work. Micro-service has its own modeler benefits. now to run this in real environment we would have
1- Host machine
2- Many Virtual Machine to start/setup individual micro-service i.e. one for each Micro-service login/security, product catalog, Account Service, Cart Server and order Server.
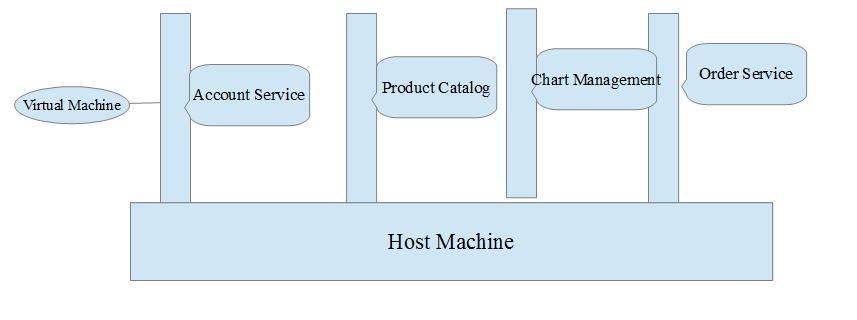
But in above scenario there is lost of memory, space , ram, resource as every Micro-service consume one virtual machine. To over come this we have the concept of Docker
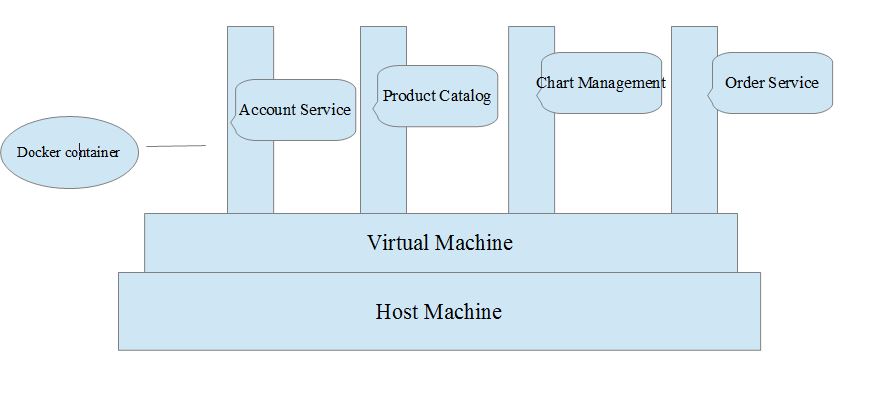
Now we might think why we need Docker concept. Lets take simple example. We have a shooing web application which has the aspect such as login/security, product catalog, Account Service, Cart Server and order Server. In best practice we prefer to have micro service either build on Spring BOOT or other frame work. Micro-service has its own modeler benefits. now to run this in real environment we would have
1- Host machine
2- Many Virtual Machine to start/setup individual micro-service i.e. one for each Micro-service login/security, product catalog, Account Service, Cart Server and order Server.

But in above scenario there is lost of memory, space , ram, resource as every Micro-service consume one virtual machine. To over come this we have the concept of Docker

As you see above now our all Micro-server is kept in Docker Container which run on the one single Virtual Machine. Due to this docker container now the micro-service did not need to reboot individual but only one VM need to boot and all service are ready to operate ... additional benefits are they did not waste RAM as now only one Virtual machine is there its same ram is shared with other Micro-service instance.
To understand Docker we need to know following below points.
1- Docker Files:- A Dockerfile is a text document/file that contains all the commands a user could call on the command line to assemble/build an image.The docker "build command" builds an image from a Dockerfile and a CONTEXT. The build’s CONTEXT is the set/collections of files at a specified location PATH or URL. The PATH is a directory on your local file-system. The URL is a Git repository location. A CONTEXT is processed recursively.
2- Docker Image :- This is file created from Docker files. It is used to execute code in docker container. A Docker image includes the elements needed to run an application as a container -- such as code, config files, environment variables, libraries and run time. If the image is deployed to a Docker environment it can then be executed as a Docker container. The docker run command will create a container from a given image. Command example
docker run hello-world
docker => this command ask installed docker to take some action
run => use to inform docker to execute image with name as hello-world and finally run execute and create hello-world container.
3- Docker Container -
- This is Rum time instance of docker file
- It is Light weight alternative of virtual machine
- It did not need ram
- It did not need to boot
- Its use host O/S.
- It did not use huge hard disc
- It is also important to note that containers differ from virtual machines (VMs), which encapsulate an entire OS with the executable code atop an abstraction layer from the physical hardware resources.
4- Docker hub - cloud base repository for storing docker images. it has both public and private repository.
5- docker files -->docker images --> docker hub --> different system download the docker images from Hub and build the environment for it.
6- Docker images are huge in size so general practice is to have docker file on docker hub or git hub and then jenkin CI server take it from there and build docker images and then docker container from it finally deploy it on different server.
7- Docker Components
- Docker Register -> storage of docker images.either on public or private repository, local or cloud, git
8- Install docker
- first install prerequisite
- second install docker-engine
- start docker engine
- download centos image from docker hub
- run centos docker iamge and create centos docker container.
9- Docket compose:- it help to run the different docker container in a single command. rather than executing single individual command to run sepearate docker container we will have one docker compose and when we run this docker compose it will run different docker container in the sequence we want. This are written in YAML files.
Installation of Docker and Docker-compose
1- follow below steps
Steps
1- sudo yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2
2- sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
3- sudo yum install docker-ce
4- sudo usermod -aG docker $(whoami)
5- sudo systemctl enable docker.service
6- sudo systemctl start docker.service
2- Then check docker is installed properly using below command
docker info
docker run hello-world
3- Finally install docker-compose use below steps
curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.23.2/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
ln -s /usr/local/bin/docker-compose /usr/bin/docker-compose
4- Check if docker-compose is installed using below command
docker-compose --version
Reference
https://github.com/NaturalHistoryMuseum/scratchpads2/wiki/Install-Docker-and-Docker-Compose-(Centos-7)
https://www.hostinger.in/tutorials/how-to-install-docker-compose-centos-7/
To understand Docker we need to know following below points.
1- Docker Files:- A Dockerfile is a text document/file that contains all the commands a user could call on the command line to assemble/build an image.The docker "build command" builds an image from a Dockerfile and a CONTEXT. The build’s CONTEXT is the set/collections of files at a specified location PATH or URL. The PATH is a directory on your local file-system. The URL is a Git repository location. A CONTEXT is processed recursively.
2- Docker Image :- This is file created from Docker files. It is used to execute code in docker container. A Docker image includes the elements needed to run an application as a container -- such as code, config files, environment variables, libraries and run time. If the image is deployed to a Docker environment it can then be executed as a Docker container. The docker run command will create a container from a given image. Command example
docker run hello-world
docker => this command ask installed docker to take some action
run => use to inform docker to execute image with name as hello-world and finally run execute and create hello-world container.
3- Docker Container -
- This is Rum time instance of docker file
- It is Light weight alternative of virtual machine
- It did not need ram
- It did not need to boot
- Its use host O/S.
- It did not use huge hard disc
- It is also important to note that containers differ from virtual machines (VMs), which encapsulate an entire OS with the executable code atop an abstraction layer from the physical hardware resources.
4- Docker hub - cloud base repository for storing docker images. it has both public and private repository.
5- docker files -->docker images --> docker hub --> different system download the docker images from Hub and build the environment for it.
6- Docker images are huge in size so general practice is to have docker file on docker hub or git hub and then jenkin CI server take it from there and build docker images and then docker container from it finally deploy it on different server.
7- Docker Components
- Docker Register -> storage of docker images.either on public or private repository, local or cloud, git
8- Install docker
- first install prerequisite
- second install docker-engine
- start docker engine
- download centos image from docker hub
- run centos docker iamge and create centos docker container.
9- Docket compose:- it help to run the different docker container in a single command. rather than executing single individual command to run sepearate docker container we will have one docker compose and when we run this docker compose it will run different docker container in the sequence we want. This are written in YAML files.
Installation of Docker and Docker-compose
1- follow below steps
Steps
1- sudo yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2
2- sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
3- sudo yum install docker-ce
4- sudo usermod -aG docker $(whoami)
5- sudo systemctl enable docker.service
6- sudo systemctl start docker.service
2- Then check docker is installed properly using below command
docker info
docker run hello-world
3- Finally install docker-compose use below steps
curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.23.2/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
ln -s /usr/local/bin/docker-compose /usr/bin/docker-compose
4- Check if docker-compose is installed using below command
docker-compose --version
Reference
https://github.com/NaturalHistoryMuseum/scratchpads2/wiki/Install-Docker-and-Docker-Compose-(Centos-7)
https://www.hostinger.in/tutorials/how-to-install-docker-compose-centos-7/



No comments:
Post a Comment