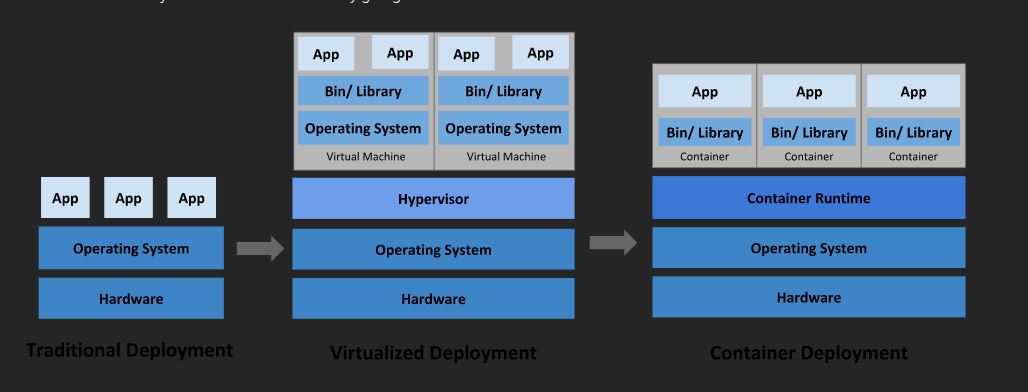
Kubernete is container management tool. This means it is used to manage container. Container manages containerized application which are deployed on them.
We have many container tool available market but the famous one is Docker. So in general Docker create container and Kubernetes manages it.
Kubernetes basically provide function that assist functionality like DSLR-MB -> deployment, scalability , load balancing, roll back, bath processing, monitoring etc.
Few of the fetures of Kubernetes as ASSS-BASH
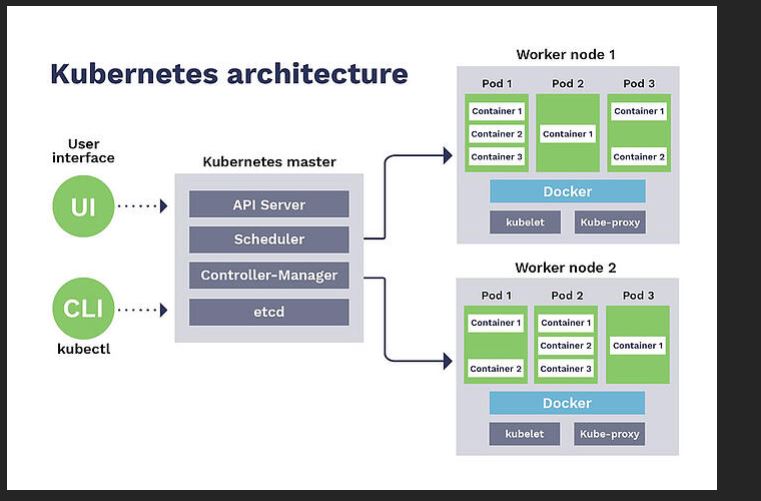
Before understanding this we nee to understand few of the concept of Kubernetes. Kubernetes does not directly work on container it works on its functional unit called as pod which is collection of containers. Each pod as one IP address and small storage unit. This storage unit can be in local system or colud or in File system.
Auto Bin Packaging:-
Kubernetes provide the optional option to the end user to define how much CPU and Memory is required by the container to run. By this way it can adjust the available machine RAM and Memory with efficient way for scaling.
Self Healing :- In this feature Kubernetes check how the node is working. If they are alive or dead if dead then restart it. If nodes not reachable delete it. If needed transfer container and pods to another nodes.
Storage :- This is small storage used in every pods for storing the information.
Servicing and Load Balancing:- Kubernetes make a collection of PODS having similar functionality into one set and provide them a service with DNS name. By doing this it can do the load balancing properly.
Batch processing :- It support the concept of batch processing i.e. where in it create a job having many pods and execute it parallel.
Auto scaling up and scale down :- for this Kubernetes create and destroy the container as on one needed.
Secrete and Configuration :- Secrete and configuration files are maintained outside the node. Secrete store the password and userid and configuration store the configuration items details. Storing out side the nodes make it easier for deployment as we did not need to create another deployment package if the userid/password or configuration changes.
Horizontal scaling:- Looking to the current usage of CPU Kubernetes can create/replica the instance/container this is called auto controller. For that purpose it provide three things .kubectl command tool, from UI and using Auto configuration. There is controller called replica controller which will fetch replica parameter from menifest files and will create and maintain that much pods already.
Now lets discuss how the Kubernetes work. As we have team which contain manager that manage the worker in same way we have cluster=team having Master node = manager and worker nodes = worker. when we say we deploy the Kubernetes we define the deploy cluster.
in single cluster we must have at least one master and at least one worker nodes. For scalability Kubernetes handle more than one master and more than one worker nodes in cluster.
Lets understand few of the architect of Kubernets
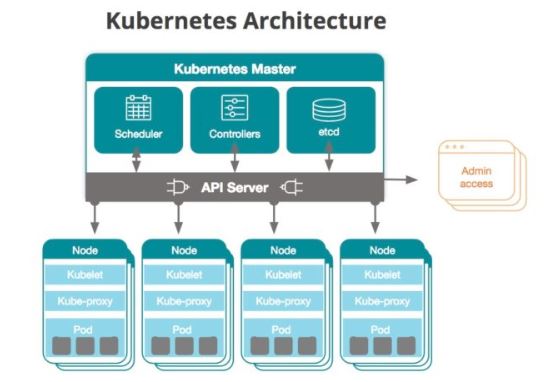
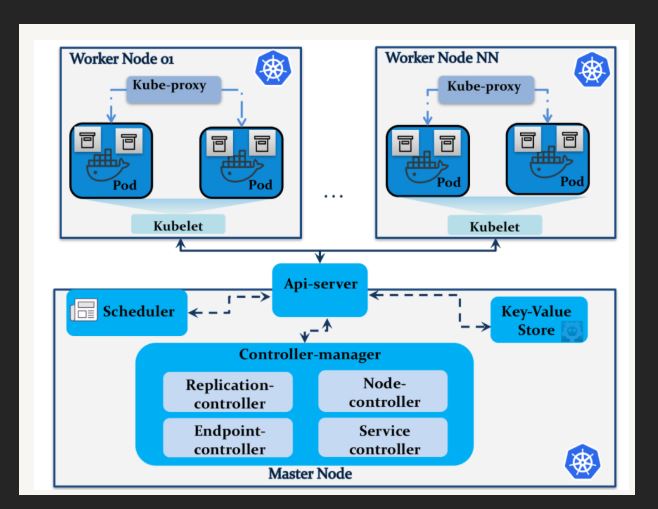
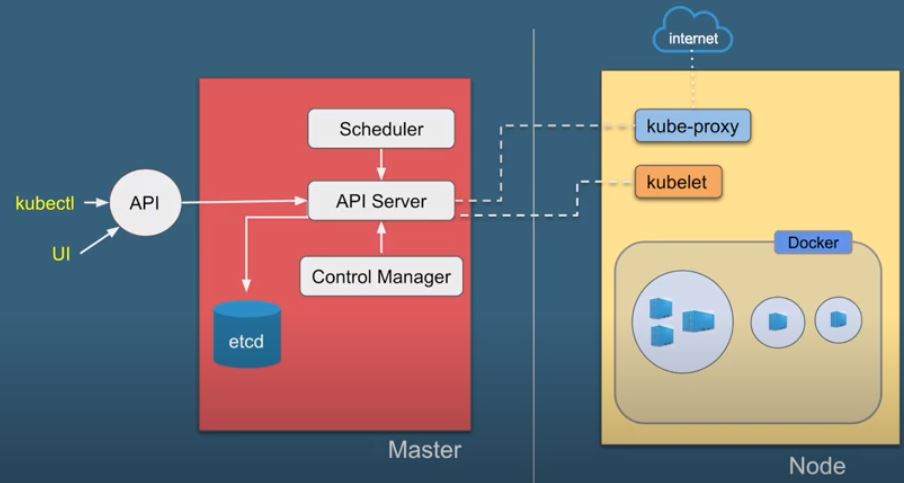
Master Nodes:- It has following part
1- Scheduler :- USe to schedule the pods and nodes.
2- API Server :- USe to communicate with different component of Master i.e. Controller and Schedule.
3- Controller manager:- It main function is to maintain the health of cluster. It check if the pods/container is live or not. If not it either try to restart it or transfer them to another nodes. It check the current status of the cluster with the configuration done in etcd and take appropriate action if needed.
It has controller like
service account :- To maintain account of the user.
End point joint controller :- Deal with communication with service that handle the pods and container.
Replica controller :- Use to maintain minimum number of pods and container.
Node controller: check the status of the pods and container.
4- ETCD - Database to store the information . It is key value data base provided by CoreOS with open source. It store the information that is required for by the Kubernetes to handle the cluster.
Worker nodes:- It has following part
1- Proxy:- This is used to expose the nodes to the out side environment.
2- Kubelet:-This is use to interact with master node using API server.
3- container:- This is the original tool machine on which our container run
Generally Kubernetes allowed to have 5000 notes in a cluster with maximum 150000 pods and 300000 container in a single cluster. Along with this a single pod cannot have more than 100 container .
Few of the diagram to understand it better taken from the source
https://blog.newrelic.com/engineering/what-is-kubernetes/
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/what-is-kubernetes/
https://medium.com/faun/kubernetes-architecture-85ad2999882a
https://blog.sensu.io/how-kubernetes-works
https://automationstepbystep.com/
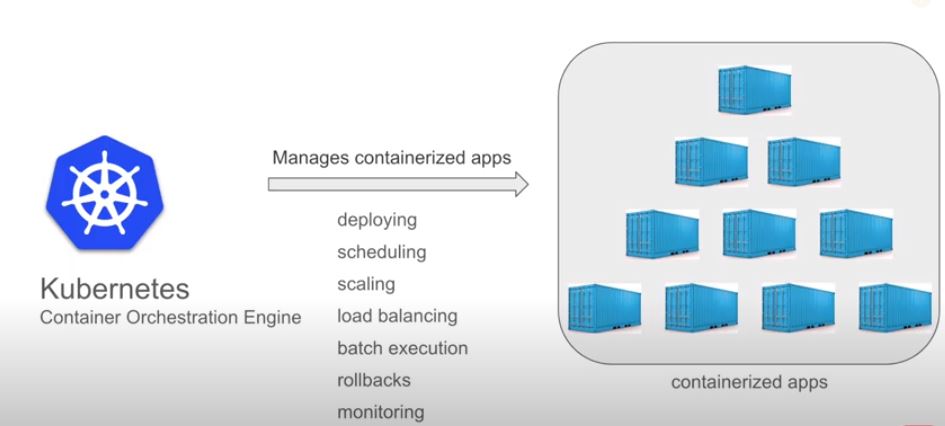
We have many container tool available market but the famous one is Docker. So in general Docker create container and Kubernetes manages it.
Kubernetes basically provide function that assist functionality like DSLR-MB -> deployment, scalability , load balancing, roll back, bath processing, monitoring etc.
Few of the fetures of Kubernetes as ASSS-BASH
Before understanding this we nee to understand few of the concept of Kubernetes. Kubernetes does not directly work on container it works on its functional unit called as pod which is collection of containers. Each pod as one IP address and small storage unit. This storage unit can be in local system or colud or in File system.
Auto Bin Packaging:-
Kubernetes provide the optional option to the end user to define how much CPU and Memory is required by the container to run. By this way it can adjust the available machine RAM and Memory with efficient way for scaling.
Self Healing :- In this feature Kubernetes check how the node is working. If they are alive or dead if dead then restart it. If nodes not reachable delete it. If needed transfer container and pods to another nodes.
Storage :- This is small storage used in every pods for storing the information.
Servicing and Load Balancing:- Kubernetes make a collection of PODS having similar functionality into one set and provide them a service with DNS name. By doing this it can do the load balancing properly.
Batch processing :- It support the concept of batch processing i.e. where in it create a job having many pods and execute it parallel.
Auto scaling up and scale down :- for this Kubernetes create and destroy the container as on one needed.
Secrete and Configuration :- Secrete and configuration files are maintained outside the node. Secrete store the password and userid and configuration store the configuration items details. Storing out side the nodes make it easier for deployment as we did not need to create another deployment package if the userid/password or configuration changes.
Horizontal scaling:- Looking to the current usage of CPU Kubernetes can create/replica the instance/container this is called auto controller. For that purpose it provide three things .kubectl command tool, from UI and using Auto configuration. There is controller called replica controller which will fetch replica parameter from menifest files and will create and maintain that much pods already.
Now lets discuss how the Kubernetes work. As we have team which contain manager that manage the worker in same way we have cluster=team having Master node = manager and worker nodes = worker. when we say we deploy the Kubernetes we define the deploy cluster.
in single cluster we must have at least one master and at least one worker nodes. For scalability Kubernetes handle more than one master and more than one worker nodes in cluster.
Lets understand few of the architect of Kubernets
Master Nodes:- It has following part
1- Scheduler :- USe to schedule the pods and nodes.
2- API Server :- USe to communicate with different component of Master i.e. Controller and Schedule.
3- Controller manager:- It main function is to maintain the health of cluster. It check if the pods/container is live or not. If not it either try to restart it or transfer them to another nodes. It check the current status of the cluster with the configuration done in etcd and take appropriate action if needed.
It has controller like
service account :- To maintain account of the user.
End point joint controller :- Deal with communication with service that handle the pods and container.
Replica controller :- Use to maintain minimum number of pods and container.
Node controller: check the status of the pods and container.
4- ETCD - Database to store the information . It is key value data base provided by CoreOS with open source. It store the information that is required for by the Kubernetes to handle the cluster.
Worker nodes:- It has following part
1- Proxy:- This is used to expose the nodes to the out side environment.
2- Kubelet:-This is use to interact with master node using API server.
3- container:- This is the original tool machine on which our container run
Generally Kubernetes allowed to have 5000 notes in a cluster with maximum 150000 pods and 300000 container in a single cluster. Along with this a single pod cannot have more than 100 container .
Few of the diagram to understand it better taken from the source
https://blog.newrelic.com/engineering/what-is-kubernetes/
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/what-is-kubernetes/
https://medium.com/faun/kubernetes-architecture-85ad2999882a
https://blog.sensu.io/how-kubernetes-works
https://automationstepbystep.com/








No comments:
Post a Comment